How to Record High Quality Audio
Recording audio for student feedback and course content is one way to add authenticity and life to your distance teaching & learning experiences. The secret to recording and delivering a high quality audio message is to access your device’s input/output settings and set the appropriate thresholds. This guide will help you set up everything you need to record audio, including the input/output settings on a Mac or PC, as well as how to monitor and set audio levels.
On a Mac
Step 1. Open System Preferences from your Apple Menu.
Step 2. Select the Sound icon from the System Preferences.
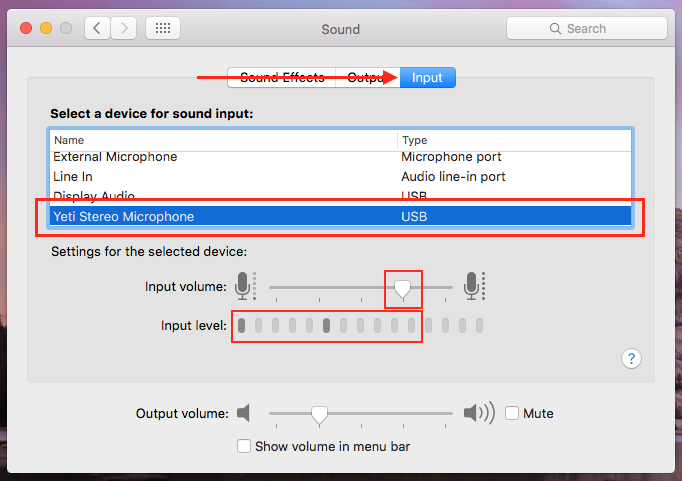
Step 3. Select the Input tab from the Sound Menu, then select your input device from the list of available devices if it is not selected already by default. Adjust the Input volume slider and observe the Input level meter while speaking in the voice you would use to record your message.
- In this example the selected input device is an external USB microphone plugged into the Mac labeled Yeti Stereo Microphone. The Input volume is set to seventy five percent. The input level will fluctuate with the cadence, intonation, and pitches of your voice.
Step 4. Record a 15 - 30 second voice sample of yourself talking or reading aloud and listen back to confirm your settings are agreeable. Repeat Step 3 as needed.
On a PC
Step 1. Locate the audio (speaker) icon in your system’s toolbar and right click to open the audio options menu.
Step 2. Select Recording Devices from the menu. A new Sound menu will appear.
Step 3. The Recording tab of this menu will be selected by default. Hover the name of the microphone you are adjusting and right click to expose an options menu, select Properties.
Step 4. Select the Levels tab of the Microphone Properties menu. You can click and drag the slider to adjust the input level, or manually enter a number in the number field. If monitoring by headphones, you should be able to hear a discernible difference as your input level is adjusted.
Step 5. Next, select the Advanced tab of the Microphone Properties menu. Select and confirm your desired sample rate and bit depth from the drop down menu. The options in the drop down will only reflect the options allowable by your microphone. Some lists may be longer with more options, others may have only one option.
- At minimum, select 2 channel, 16 bit, 44100 Hz (CD Quality) as this is the industry standard for audio recordings. For a video project, or for audio that may be added to a video project, select 2 channel, 16 bit, 48000 Hz (DVD Quality) as this is the industry standard minimum for video.
- Click Apply to confirm all changes, otherwise click OK to close the menu and confirm settings.
Step 6. After closing the Microphone Properties menu, the Recording tab of your sound menu will still be open. You should now be able to confirm visually that your microphone is receiving signal when you talk.
Best Results & Troubleshooting
Mac Only
Monitor the Input level meter for a few seconds while you speak to see if the level is appropriate. Visually, if the meter shows levels reaching the end of the meter’s length, lower your Input volume setting.
Mac and PC
Auditorily, if you hear audio in your headphones or speaker that sound scratchy, distorted or makes you feel uncomfortable, lower your input volume setting. Wearing headphones is the recommended method for monitoring the Input level.
Input volume on a Mac, and Microphone level on a PC are actually representations of input sensitivity or the level at which your device is listening for sounds. At this point, you are adjusting your microphone’s ability to hear you. If you speak softly, the Input level may appear low, causing you to raise your Input volume unnecessarily. Raising up the sensitivity to accommodate a soft voice will not only increase sensitivity for your voice, but also gather all other sounds in proximity. Speaking louder/softer, and moving closer/further from the device are ways to adjust your input volume and for your voice to compete with extraneous noises, if any (e.g. air conditioning, other distant background conversations, the faint sounds of your neighbor’s lawn mower).
Isolate your voice for recordings by closing windows and doors to your workspace. Notify others nearby that you need them to be quiet or to keep a distance from your recording space for a short while. Turn of any devices that emit electrical noises or notification sounds.
