What can data science do for business today?

What do you think of when you hear the term data science? Drawing on popular media mentions of the term, you might think it is a field that pushes the limits of information technology with conversational agents and intelligent robots, making machines behave like people.
The association of data science with machine learning and artificial intelligence cannot be denied. These are exciting areas of development, deserving of media hype.
What can data science do for business today?
To put data science into practice, we can gather data from the daily activities of business, we can analyze business processes and look for opportunities to improve those practices.
 Wil van der Aalst, a prominent business researcher, has long argued for an alignment of data science and process science. European academics following his lead offer courses in business process mining and analytics. At Northwestern, we see great value in using the methods of data science to improve business processes.
Wil van der Aalst, a prominent business researcher, has long argued for an alignment of data science and process science. European academics following his lead offer courses in business process mining and analytics. At Northwestern, we see great value in using the methods of data science to improve business processes.
With more than forty courses and five specializations to choose from, students in Northwestern’s master's in data science (MSDS) program can tailor their studies to fit personal interests and career objectives. For students seeking technology leadership and management positions, there are many business-focused data science courses. Let’s highlight a few.
- MSDS 450 Marketing Data Science. This course introduces methods for measuring consumer preferences and predicting consumer choices. Marketing data science can guide decisions about new product design and pricing. Each company’s products and services compete with the products and services of other companies. Marketing strategy and tactics should be informed by an understanding of markets and the competition.
- MSDS 460 Decision Analytics. What should we make? How should we make it? When should we make it? And how can we get what we make to the buyer who needs it? Basic questions like these can be informed by materials, labor, and transportation costs and by anticipated sales prices. Mathematical programming methods introduced in this course show how to answer these questions.
- MSDS 472 Management Consulting. Productive data scientists, while steeped in the jargon of analytics and modeling, need to communicate with nontechnical people. Key to putting data science into practice is the ability to ask the right questions and listen carefully to the answers that management provides. Productive data scientists become trusted consultants, developing relationships with management over time.
- MSDS 474 Accounting and Finance for Technology Managers. It is sometimes said that accounting is “the language of business.” To communicate effectively with business managers, data scientists need to speak the language of business. They need to understand the basic principles of accounting and finance.
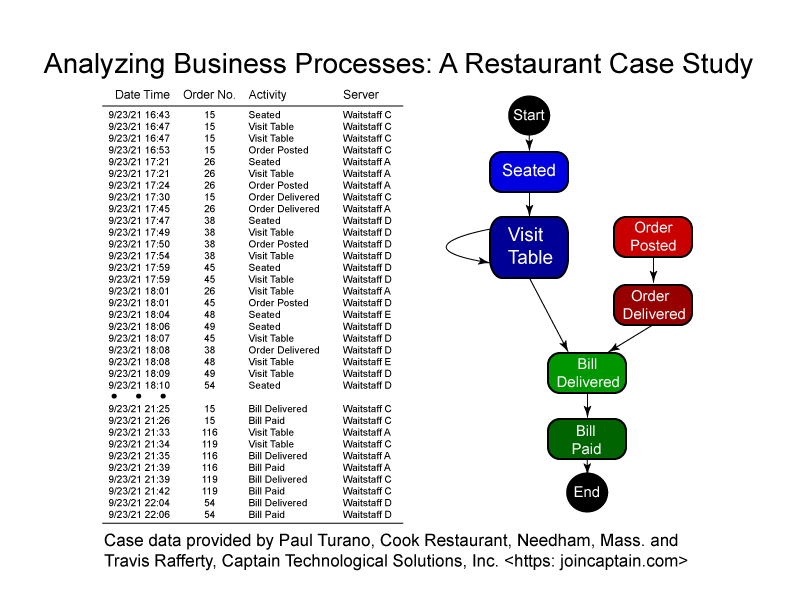
- MSDS 476 Business Process Analytics. To improve business processes, we must first understand business processes as they are carried out today. Data from operations, recorded in time-stamped logs of activities and their associated costs, represent essential information for business management. Business process analytics involves working with activity logs, learning from the information they contain, and making recommendations to management about process improvements.
This figure shows a partial activity log from a full-service restaurant case study. Using activity logs like this, scientists trained in methods of business process analytics can identify common processes, as well as potential areas for improving workforce staffing and customer service.
Business-related data science courses at Northwestern
A case study approach to teaching is common across business courses in Northwestern’s data science curriculum. Students learn by addressing real business problems and their accompanying data sets.
Looking across the data science curriculum, we see many courses with a business focus: MSDS 403 Data Science and Digital Transformation, MSDS 470 Technology Entrepreneurship, MSDS 475 Project Management, MSDS 480 Business Leadership and Communication, and MSDS 485 Data Governance, Ethics, and Law.
Many data science students pursue the Analytics Management specialization within the data science master’s program. For students reluctant to commit to the twelve-course master’s program, there is a four-course graduate certificate in Analytics Management.
For students interested in start-ups and new business ventures, Northwestern offers the Technology Entrepreneurship specialization within the master’s program, as well as the Technology Entrepreneurship graduate certificate.
An overview of data science careers is provided under Data Scientist, Data Engineer, or Technology Manager: Which Job is Right for You?
For corporations interested in training groups of employees in data science and information technology skills, Northwestern also offers data science and technology education tailored for organizations.
Data Science Specializations
The Northwestern data science program offers five specializations. Analytics and Modeling and Artificial Intelligence are most closely aligned with the data scientist role. Students seeking technology management roles may select Analytics Management or Technology Entrepreneurship. And students who want to understand how to build end-to-end information systems can choose the Data Engineering specialization.
To learn more about what data science can do for business, listen to the presentation, "Putting Data Science into Practice" by Northwestern Data Science Faculty Director Tom Miller.
